Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email already exists
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
Email format error
Email cannot be empty
Email does not exist
6-20 characters(letters plus numbers only)
The password is inconsistent
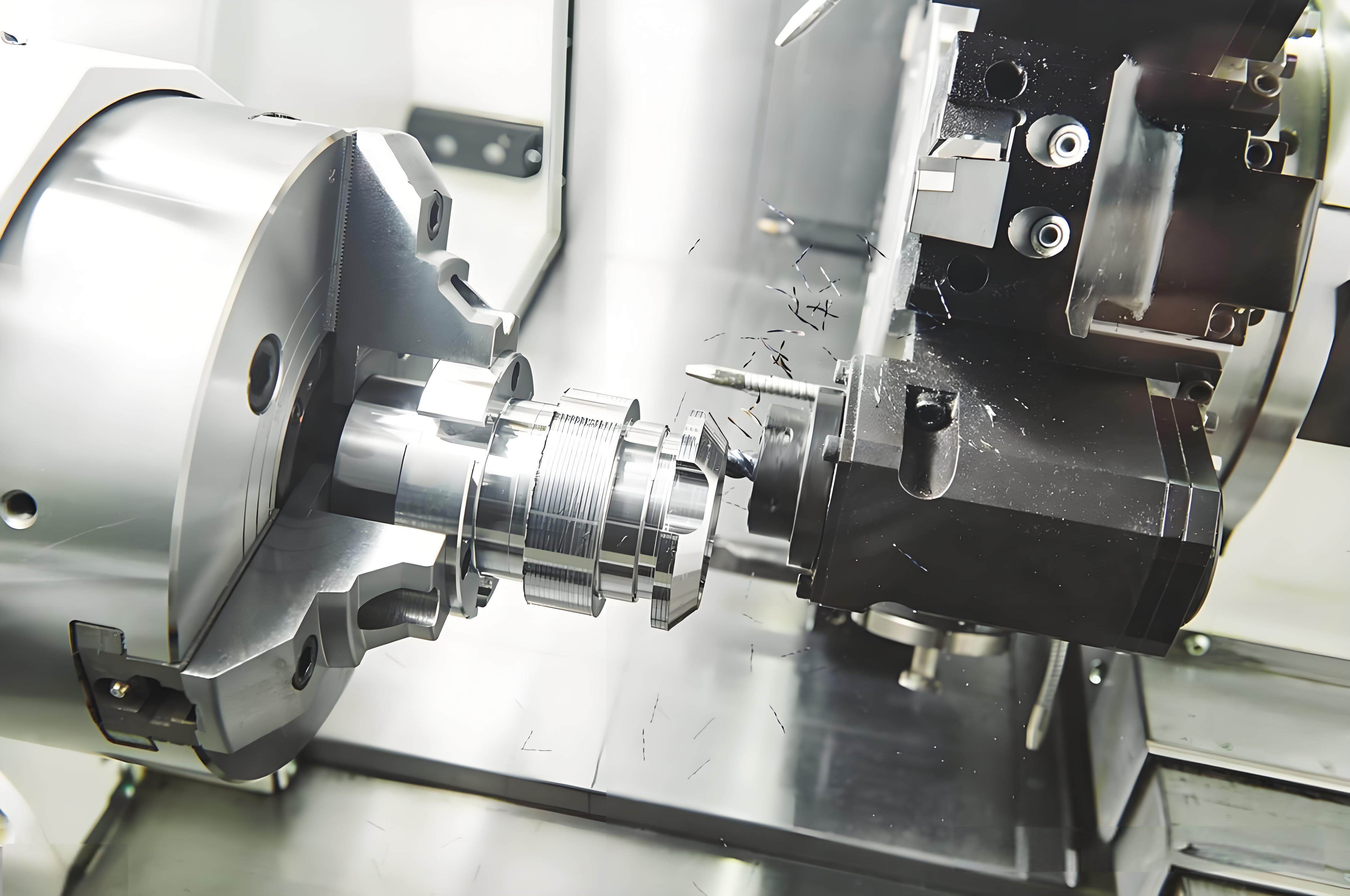


CNC Machine Processing: Advanced Techniques and Future Trends
Introduction to CNC Machine Processing
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine processing stands as a cornerstone of contemporary manufacturing, delivering unmatched precision and efficiency. Whether engaged in small-batch bespoke part fabrication or large-scale production, CNC guarantees meticulous parts processing with unwavering quality, irrespective of complexity. It adeptly manages a vast array of operations, from rudimentary 2D cuts to intricate 3D engravings, affording manufacturers in diverse sectors—such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices—remarkable flexibility. By harnessing CNC machine processing, manufacturers can produce exceptionally accurate components by translating CAD/CAM designs into G-code, which orchestrates the machine’s movements. Each nuanced instruction is paramount, ensuring precise tool navigation and product uniformity.
Key CNC Processing Techniques
A plethora of fundamental CNC processes exists, each tailored for distinct applications. Mastery of these techniques is imperative for enhancing both production efficiency and product quality.
1. Explanation of CNC milling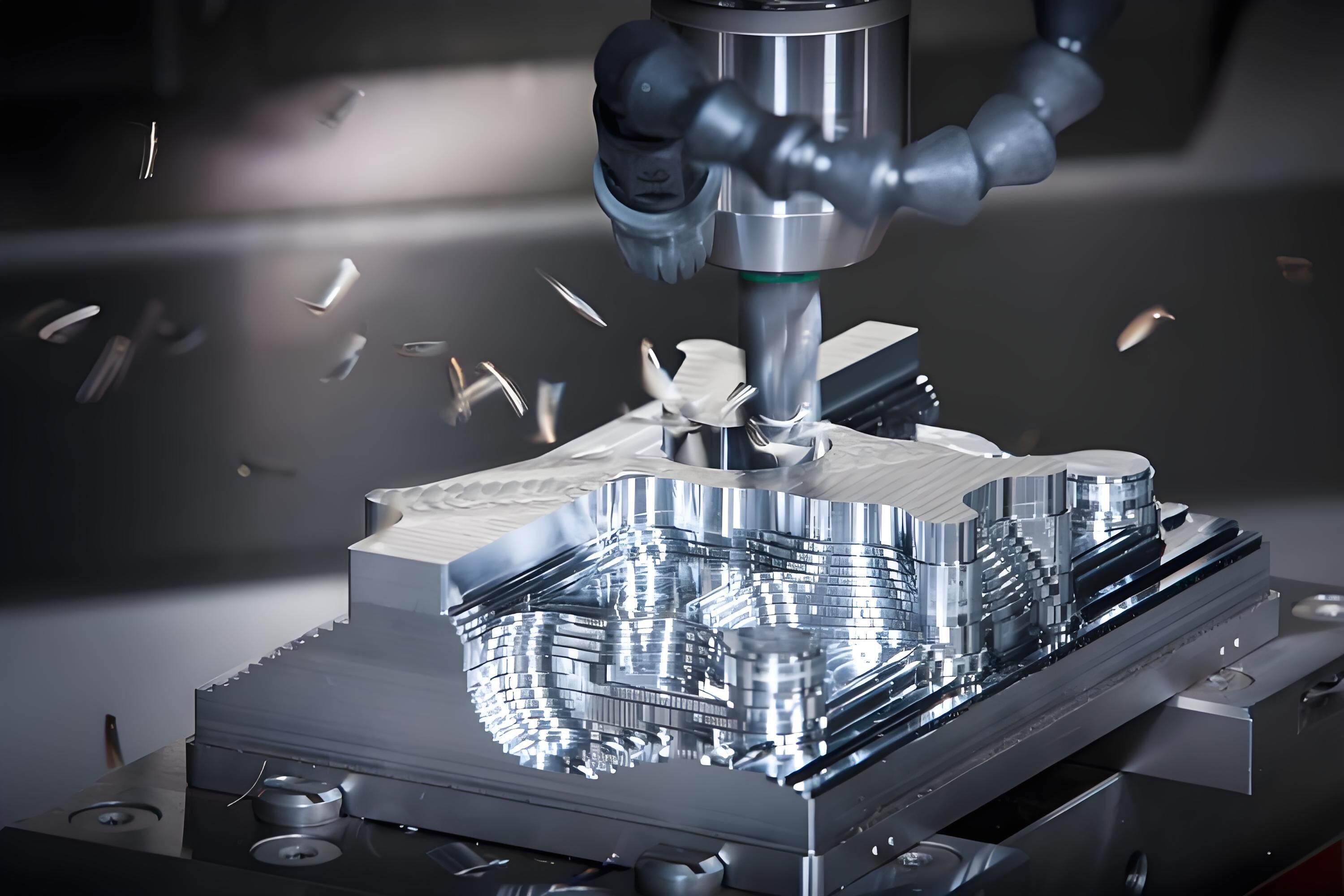
CNC milling employs rotary cutters to excise material, sculpting elaborate shapes, planes, or apertures. It operates across multiple axes (3-axis, 5-axis), rendering it one of the most adaptable methodologies in CNC machine processing. Advanced milling techniques empower manufacturers to fabricate highly complex components with astonishing accuracy.
2.Overview of CNC Turning 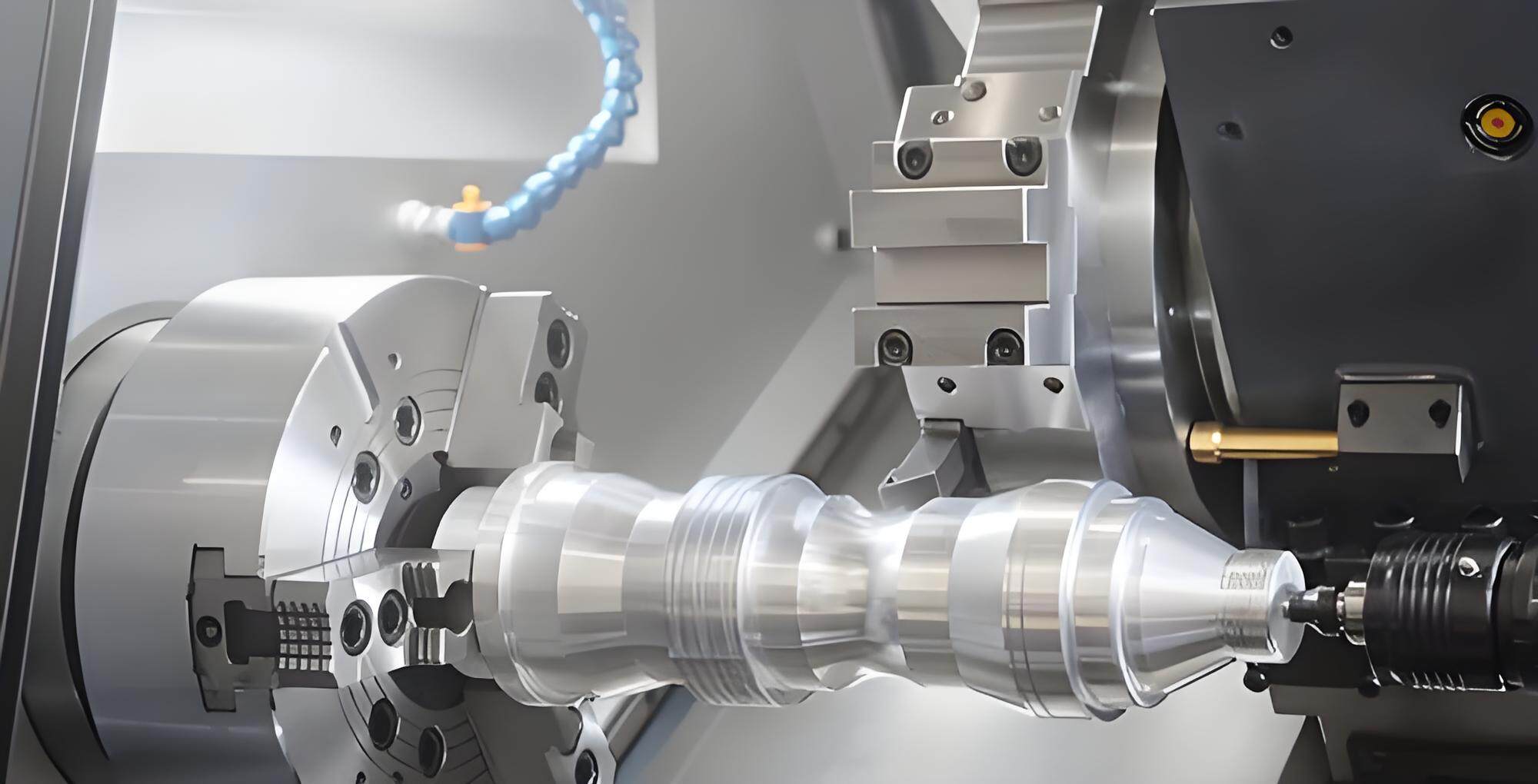
CNC turning excels in the production of cylindrical components, such as shafts, bushings, and hubs. In this process, the workpiece rotates while a stationary tool executes the cutting. This method guarantees impeccable circular symmetry and high dimensional fidelity, making it indispensable for components necessitating precision.
3. Introduction to CNC drilling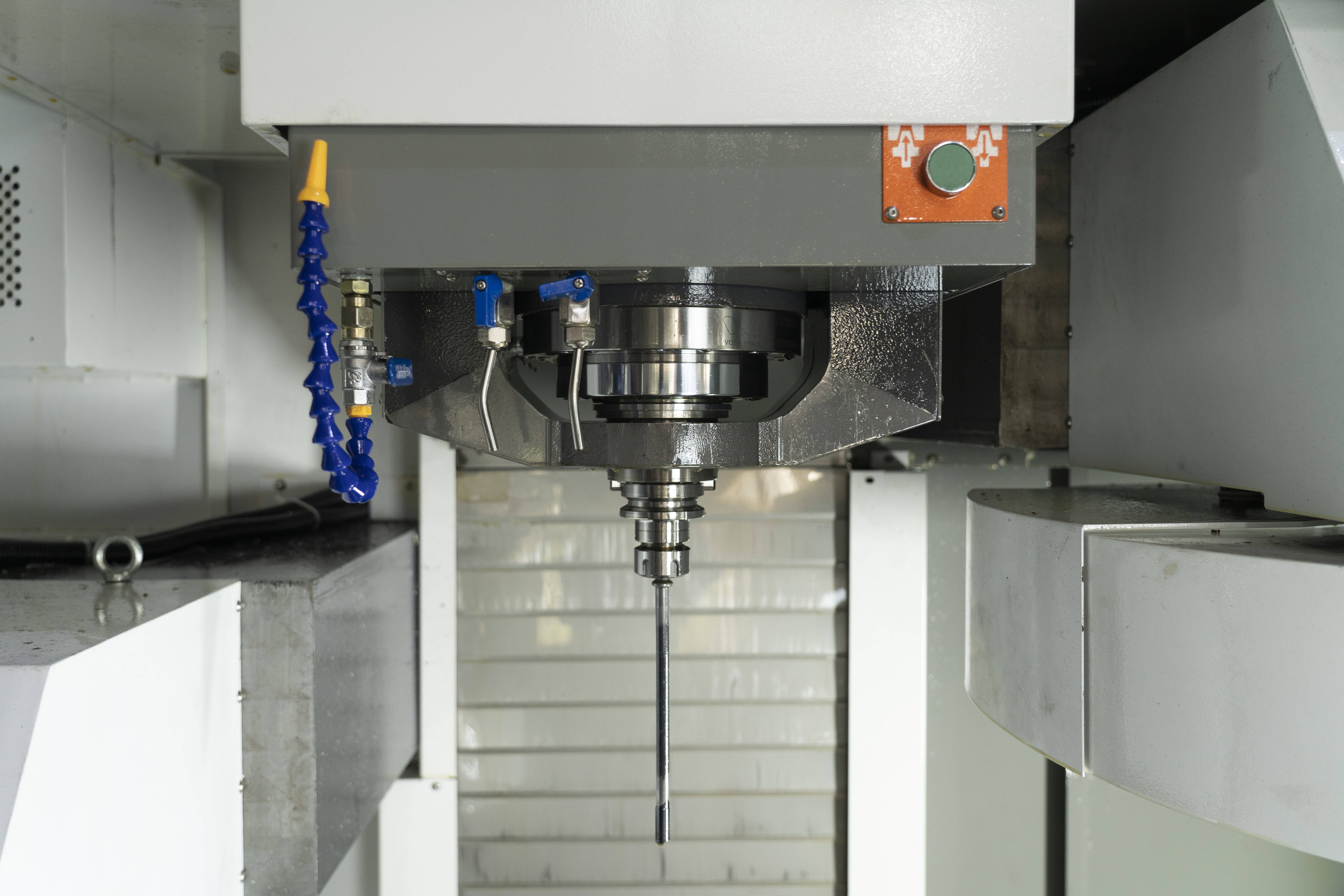 
CNC drilling apparatuses generate precise apertures with controlled depth and diameter, crucial in sectors where accuracy in hole placement is paramount. The aerospace and automotive industries depend on CNC drilling to adhere to stringent tolerance specifications.
4. CNC Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
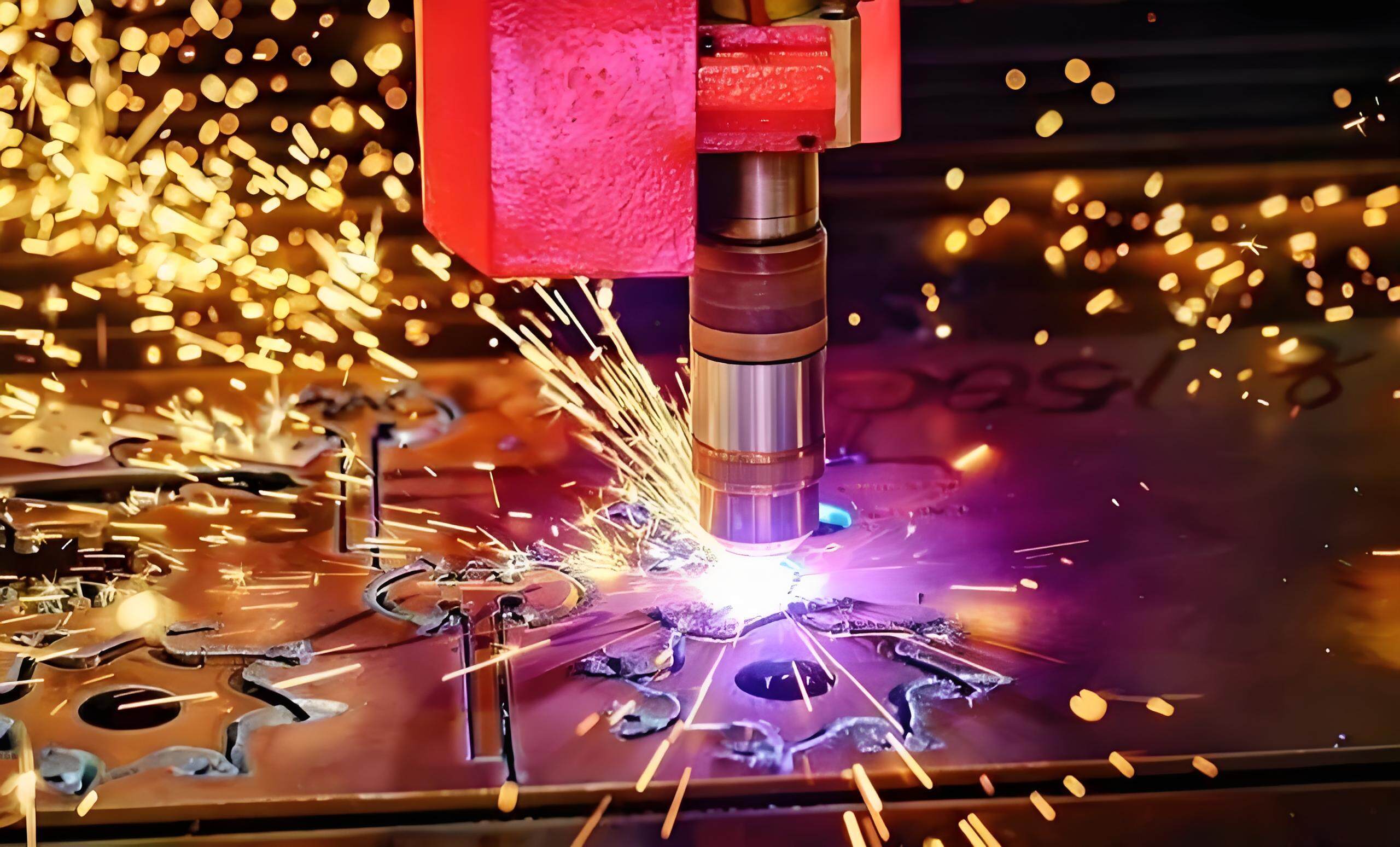 CNC EDM
CNC EDM For materials that are exceptionally hard or geometrically intricate, CNC EDM frequently emerges as the preferred technique. EDM operates by utilizing electrical discharges to erode material, facilitating precision shaping of metals that resist conventional cutting methods.
Optimization Strategies in CNC Parts Processing
Optimization is vital for amplifying the productivity and efficacy of CNC operations. Below are several pivotal strategies that not only enhance the production cycle but also curtail costs and prolong equipment lifespan.
1. Tool Path Optimization
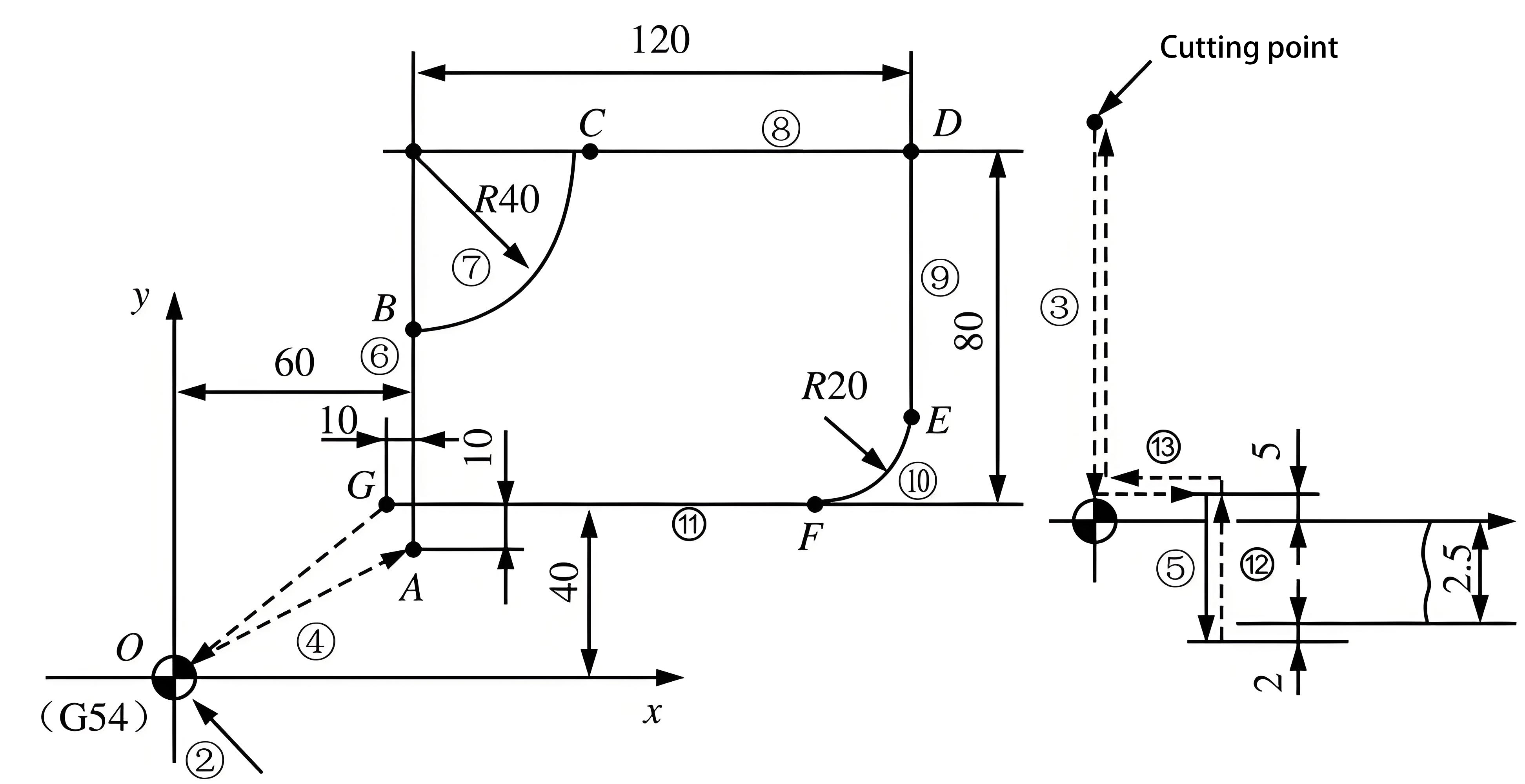
Three major tool parameter compensation
Refining the tool path stands as one of the most efficacious methods to bolster CNC performance. By employing CAM software, manufacturers can simulate the entire machining process prior to production, minimizing tool collisions, diminishing idle time, and augmenting machining accuracy. Efficient tool paths reduce machining duration and enhance surface finish, yielding a mutually beneficial outcome.
2. Choosing the Right Tooling Material and Geometry
The selection of tooling material profoundly influences the quality of the produced parts. Harder materials, such as carbide tools, excel in cutting through tough metals, while high-speed steel (HSS) is preferable for softer substrates. Furthermore, tool geometry—encompassing rake angle and relief angle—should be optimized for specific materials to mitigate wear and enhance cutting efficiency.
3. Fine-Tuning Cutting Parameters
Cutting parameters, including feed rate, spindle speed, and depth of cut, require meticulous control to achieve optimal results. Elevated feed rates can boost productivity but may also precipitate excessive tool wear, while diminished feed rates might yield subpar surface finishes. Striking the right equilibrium between velocity and precision is essential for prolonging tool life and attaining superior output.
4. Vibration and Noise Control
Excessive vibrations during machining can culminate in diminished tool longevity, inaccurate parts, and inferior surface finishes. Mitigating vibrations through appropriate work-holding, optimizing cutting parameters, and employing dampening tools can significantly enhance the final part quality. Additionally, utilizing suitable coolants can aid in regulating both noise and temperature, further amplifying performance.
Future Trends in CNC Parts Processing
As the industry progresses, CNC machine processing is evolving into a more intelligent, automated, and interconnected domain. Here are some trends that are sculpting the future of parts processing.
Summarize
CNC machine processing remains at the forefront of innovation in modern manufacturing, continually adapting to meet the demands of an ever-evolving landscape. As manufacturers embrace these advanced techniques and optimization strategies, they position themselves to harness the full potential of CNC technology.
The integration of smart systems and adaptive controls not only enhances operational efficiency but also fosters a culture of continuous improvement. By leveraging data analytics and real-time monitoring, manufacturers can make informed decisions that drive productivity and quality. The ability to predict maintenance needs and adjust processes dynamically ensures that production lines remain agile and responsive to market fluctuations.
Moreover, the synergy between CNC machining and additive manufacturing heralds a new era of design possibilities. This hybrid approach allows for the creation of complex geometries that were previously unattainable, opening doors to innovative product designs and applications. Industries such as aerospace and healthcare stand to benefit immensely from this convergence, as it enables the production of lightweight, high-strength components that meet stringent regulatory standards.
As we look to the future, the role of CNC machine processing will only become more pronounced. The advent of Industry 4.0, characterized by increased automation and interconnectedness, will further enhance the capabilities of CNC systems. Manufacturers who invest in these technologies will not only improve their operational efficiency but also gain a competitive edge in a global marketplace.

